Phenotypic ratio 194058-Phenotypic ratio of f2 generation
Write the amount of homozygous dominant (AA) and heterozygous () squares as one phenotypic group Count the amount of homozygous recessive (aa) squares as another group 5a Write the result as a ratio of the two groups A count of 3 from one group and 1 from the other would give a ratio of 31 Punnet Square RatioN The observable physical or biochemical characteristics of an organism, as determined by both genetic makeup and environmental influences The expression of a specific trait, such as stature or blood type, based on genetic and environmental influencesFor a variety of reasons, the phenotypic ratios observed from real crosses rarely match the exact ratios expected based on a Punnett Square or other prediction techniques There are many possible explanations for deviations from expected ratios Sometimes these deviations are due to sampling effects, in other words, the random selection of a nonrepresentative subset of individuals for observation
Q Tbn And9gcr01m Vckbdnhlocf2b0xuudahgaekzu5mgcymop Dgflvpczl9 Usqp Cau
Phenotypic ratio of f2 generation
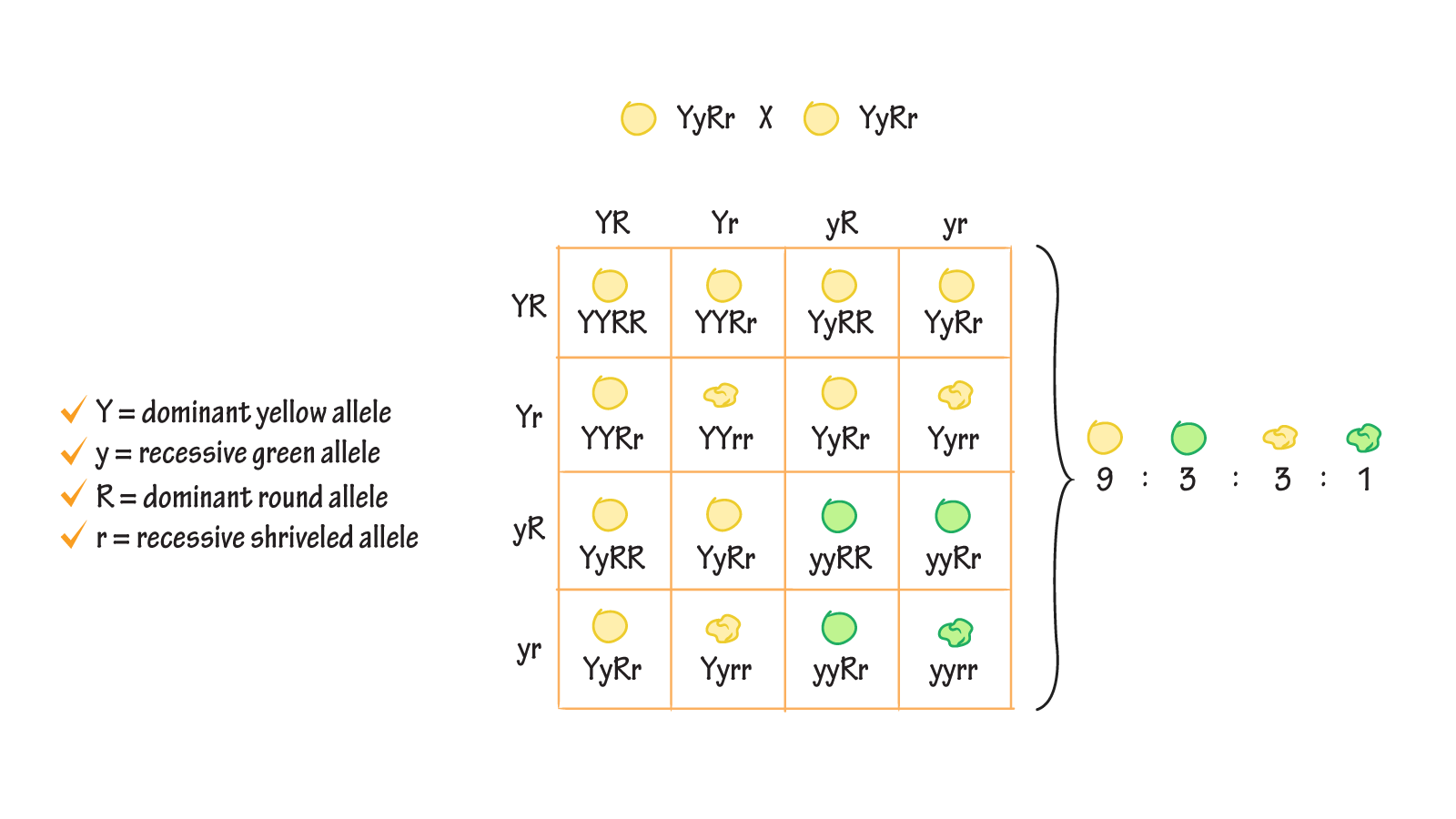
Phenotypic ratio of f2 generation-Typical Phenotypic Ratio for a Dihybrid Cross is 9331 The Phenotypic ratio will explain the genotypic ratio when you you solve a Dihybrid CrossA phenotypic ratio of 9331 A phenotypic ratio of 9331 is predicted for the offspring of a SsYy x SsYy dihybrid cross 9 spherical, yellow 3 spherical, green 3 dented, yellow 1 dented, green The Biology Project


Punnett Squares
Its phenotypic ratio is 9331, where 9 plants have all dominant characteristics and 1 plant has all recessive characteristic (Valid only for Angiosperms / similar sexually reproducing organisms) According to Mendel's statement, between the alleles of both these loci, there is a relationship of completely dominant recessive traitsA phenotype ratio is the number of offspring with a certain phenotype after a genetic cross, like 3 purple flowers 1 white flower For example, Let's say purple is the dominant trait and white isPhenotypic ratio 3 Y 1 yy Mendel's experiments were consistent with these predictions Since then, thousands of other experiments involving many different traits in many different plants and animals have been shown to be consistent with these predictions, which are based on Mendel's law of segregation
A ratio that shows the different outcomes you can get from a genetic cross A ratio that shows the varied outcomes that results from a genetic cross and is based on physical appearance alone ForLearn how to solve Punnett squares In this video, I review how to write genotype and phenotype ratios and percentsKey topics covered include solving a monoPhenotypic Ratios 31 121 121 series of 31 ratios monohybrid cross (complete dominance) black or white monohybrid cross (incomplete dominance) black, white, or gray monohybrid cross (codominance) black, white, or black/white multiple alleles (dominance is relative) black, blue, white,
The proximate cue for this plastic response is the ratio of red to farred light (RFR ratio), which is transduced primarily via phytochrome light receptors In this case, the environmental cue that induces the phenotypic response (RFR ratio) and the environmental stress that the response functionally accommodates (aboveground competition) are distinctSelect Page phenotypic ratio of dihybrid cross by Feb 19, 21 Uncategorized 0 comments Feb 19, 21 Uncategorized 0 commentsThe phenotypic ratio is the number of times a specific combination of alleles appears in the predicted phenotypes of any offspring Genetic information relating to the studied trait must be known It is also possible to work out which parent alleles are dominant or recessive by studying the phenotypes of their offspring
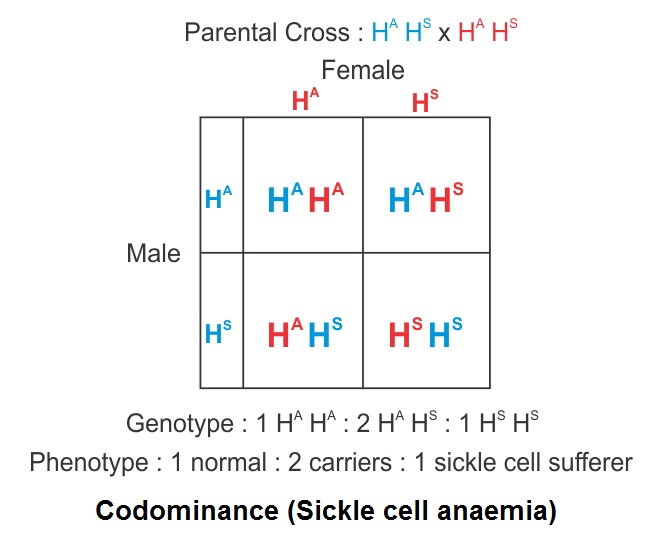


What Is The Phenotypic Ratio Of F1 Progeny In Codominance Biology Topperlearning Com Zkhr84gg


Punnett Squares
Phenotypic ratio is 31 or 121 or 21 ¥If two genes are involved in the trait, then the dihybrid phenotypic ratio is 9331 or some permutation (943 or 97 or 1231) "The 1/16 class is always the double homozygous recessive" Look for internal 31 ratios, which will indicate dominance/recessive relationships for alleles within a geneIt's easy to calculate that the genotypic ratio is 0505, which is equal to 11 What is the phenotypic ratio?The phenotype ratio is 40 (4 purple 0 white) meaning there are 100% purple and 0% white flowers To keep things simple, you do not need to reduce the ratio to the lowest terms (in other words, the sum of the numbers in the ratio should equal the number of boxes in the Punnett Square) It would not, however, be incorrect to reduce the genotype ratio to 110 and the phenotype ratio to 10



Determining Genotypes And Phenotypes Using Punnett Squares Free Homework Help



Chapter 3 Flashcards Quizlet
Expected F2 Phenotypic Ratio = 1/4 yellow 3/4 purple d Both a and care true A pedigree analysis is useful To study the pattern of inheritance of traits in families b To observe recessive and dominant traits To predict the possible traits in a future generation d All of the above are true 14Phenotypic ratio is 31 or 121 or 21 ¥If two genes are involved in the trait, then the dihybrid phenotypic ratio is 9331 or some permutation (943 or 97 or 1231) "The 1/16 class is always the double homozygous recessive" Look for internal 31 ratios, which will indicate dominance/recessive relationships for alleles within a geneThis means that both parents have recessive alleles, but exhibit the dominant phenotype The phenotype ratio predicted for dihybrid cross is 9331 Of the sixteen possible allele combinations Nine combinations produce offspring with both dominant phenotypes Three combinations each produce offspring with one dominant and one recessive phenotype



Answered 2 Show The Cross And Provide Full Bartleby



8 9 7 Phenotypic Ratio In F2 Generation Download Scientific Diagram
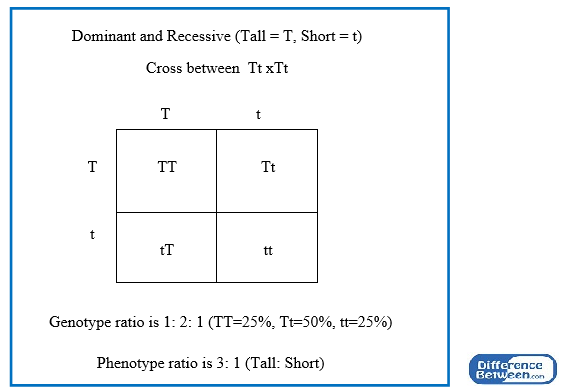
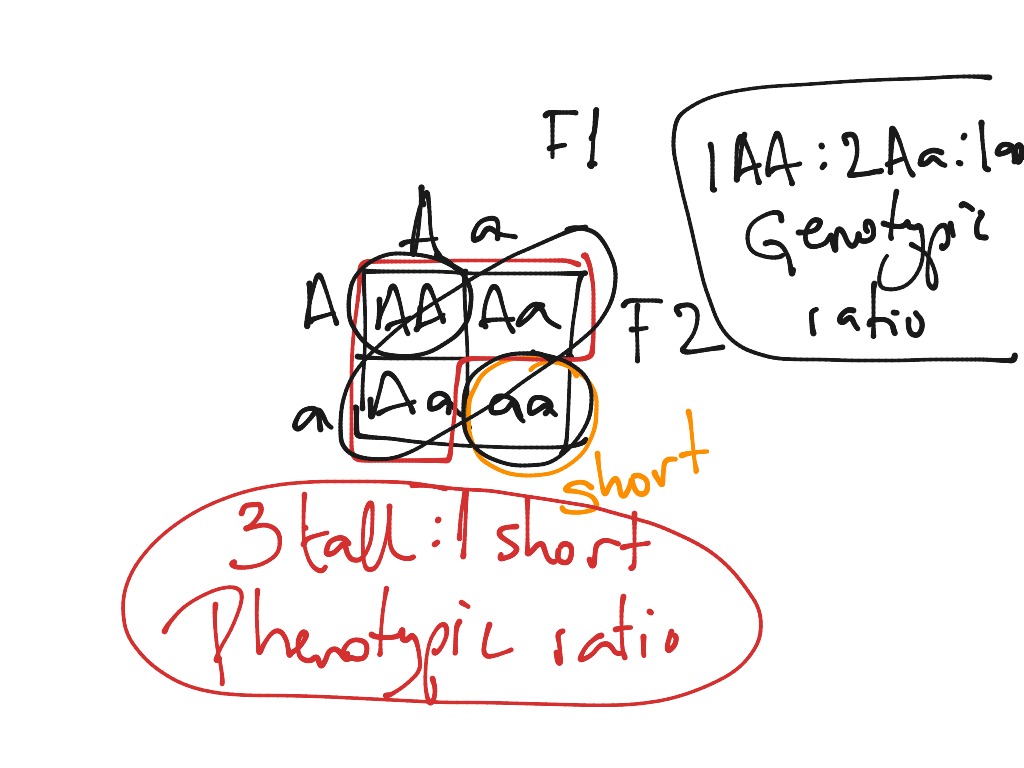
So, the phenotypic ratio is 31 (tall vs short) The totally recessive individuals are highly useful in genetics Whenever you see one, you automatically know the entire genotype (ie both alleles) for that genePhenotypic ratio Make a list of all the different phenotypes (physical characteristics In you problem this would be Tall/Black = 9, and Tall/white = 3, short/Black = 3, and short/white = 1 The phenotypic ratio would therefore be 9331The ratio of the phenotypes is 31, typical for a monohybrid cross Eurlex19 Mortality (and abnormal appearances), time to NF stage 62 (larval sample), thyroid histology assessment (larval sample), growth (weight and length), liversomatic index (juvenile sample), genetic/phenotypic sex ratios (juvenile sample), histopathology for gonads, reproductive ducts, kidney and liver (juvenile sample) and plasma vitellogenin (juvenile sample, optional)



Genotypes Genotypic Ratio Phenotypes Phenotypic Ratio 13 In The Land Of Oompah Course Hero


Www Greeleyschools Org Cms Lib2 Co Centricity Domain 5219 Punnett sq cheat sheet Pdf
Phenotype for bb = Ab;The expected phenotypic ratio of the progeny of a SsYy x ssyy test cross is a 9331 b 31 c 1111 d 122 e 3113 2Each genotype for an codominant trait has its own phenotype However the heterozygote has both parental phenotype the parents The phenotypic ratios for overdominant traits are the same as for incompletely dominant traits Therefore, the expected phenotypic ratios among the F 2 progeny are 1/4 A antigen (A 1 A 1) 1/2 A and B antigen (A 1 A 2)


Q Tbn And9gcr01m Vckbdnhlocf2b0xuudahgaekzu5mgcymop Dgflvpczl9 Usqp Cau


Www Madison K12 Ct Us Fs Resource Manager View Add Adb5 4e3b B525 57d27e2a377d
Genotypic ratios refer to the distribution of the different allelic combinations irrespective of if they are expressing the same trait phenotypically While phenotypic ratio is the distribution of the possible outward expression of the genesIn any case where the parents are heterozygous for both traits ( x ) you will always get a 9331 ratio 9 is the number for the two dominant traits, 3 is the number for a dominant/recessive combination, and only 1 individual will display both recessive traits Another way to determine the ratios is to do it mathematicallyPhenotypic ratio Make a list of all the different phenotypes (physical characteristics In you problem this would be Tall/Black = 9, and Tall/white = 3, short/Black = 3, and short/white = 1 The phenotypic ratio would therefore be 9331



How To Find A Phenotypic Ratio Of A Cross Dihybrid With Double Homozygous Recessive Youtube


Monohybrid Cross Problem Set
The genotypic ratio for this cross is written 121 In animals and plants, each gene has 2 alleles or variations, one from each parent When male and female gametes come together (cross) all the phenotype variations for the offspring are predicted using the Punnett square gridIts phenotypic ratio is 9331, where 9 plants have all dominant characteristics and 1 plant has all recessive characteristic (Valid only for Angiosperms / similar sexually reproducing organisms) According to Mendel's statement, between the alleles of both these loci, there is a relationship of completely dominant recessive traitsThe phenotype ratio is 40 (4 purple 0 white) meaning there are 100% purple and 0% white flowers To keep things simple, you do not need to reduce the ratio to the lowest terms (in other words, the sum of the numbers in the ratio should equal the number of boxes in the Punnett Square) It would not, however, be incorrect to reduce the genotype ratio to 110 and the phenotype ratio to 10


Master Frameset


Http Www Deercreekhs Org Userfiles Servers Server File Bush Mendelian genetics study guide Pdf
The key difference between phenotype and genotype ratio is that the phenotype ratio is the relative number of or the pattern of the offspring manifesting the visible expression of a particular trait while the genotype ratio is the pattern of offspring distribution according to the genetic constitution Phenotype and genotype are two terms that use to describe the characteristics of an organism in geneticsThe phenotypic ratio is 31 Threefourths of the offspring will have purple flowers (PP, Pp) and onefourth will have white flowers (pp) In a cross between a heterozygous parental plant and a recessive plant, the expected genotypes observed in the offspring will be (Pp) and (pp)Each of the genotypes of the offspring corresponds to a different phenotype SsYy are smooth, yellow seeded Ssyy are smooth, green seeded ssYy are dented, yellow seeded ssyy are dented, green seeded These phenotypes will appear in a predicted 11s11 ratio The Biology Project



Genotypic Ratio Phenotypic Ratio This Is An Example Of Incomplete Or Course Hero
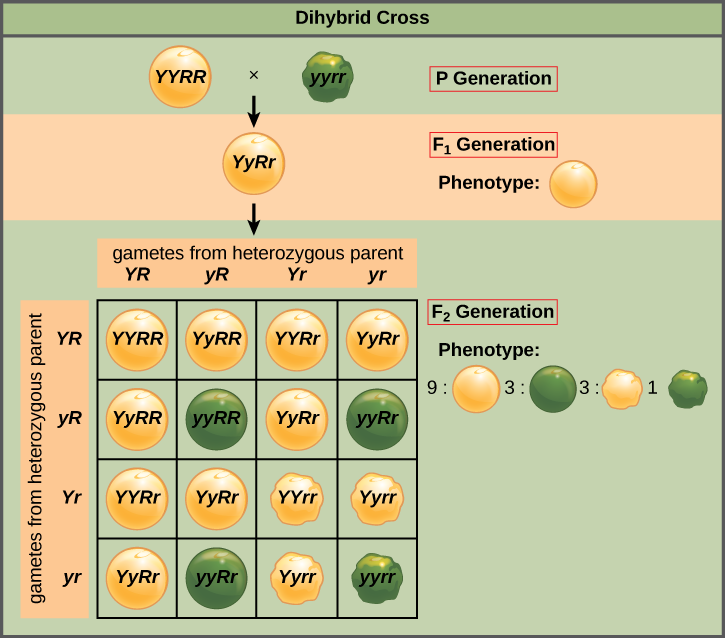


8 2 Laws Of Inheritance Concepts Of Biology 1st Canadian Edition
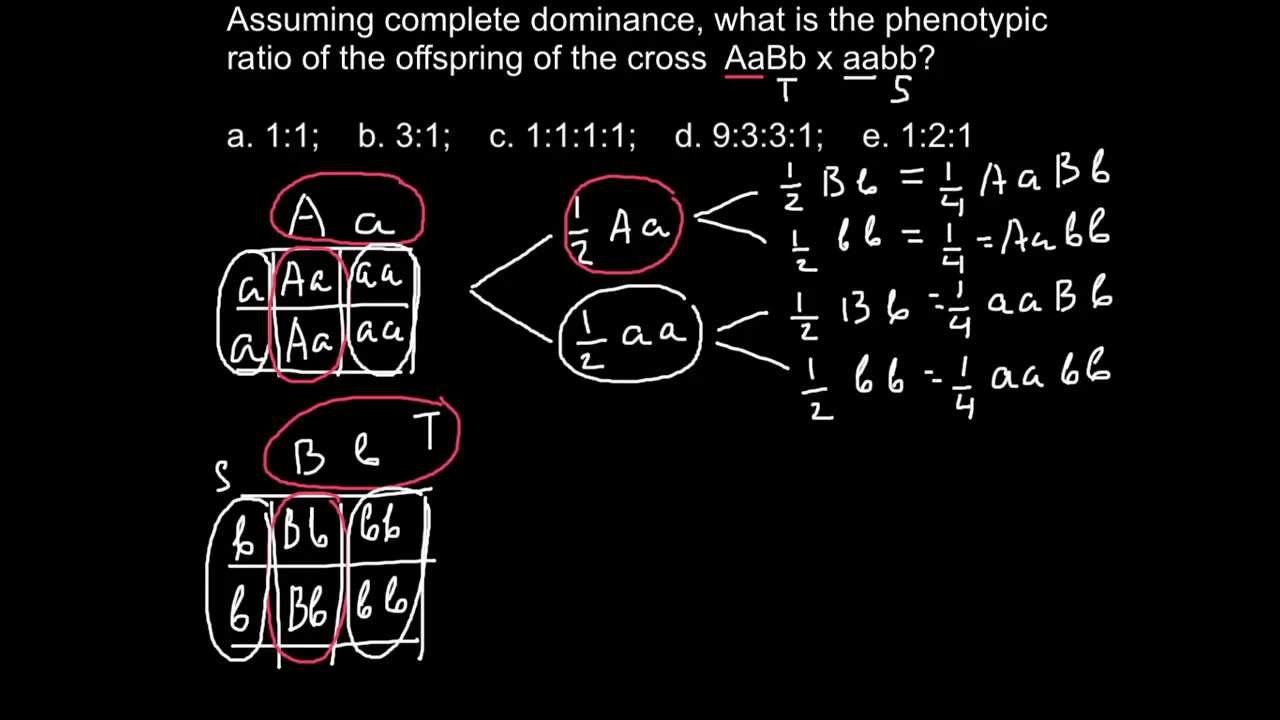
For a variety of reasons, the phenotypic ratios observed from real crosses rarely match the exact ratios expected based on a Punnett Square or other prediction techniques There are many possible explanations for deviations from expected ratios Sometimes these deviations are due to sampling effects, in other words, the random selection of a nonrepresentative subset of individuals for observationPhenotype for aabb = ab Now we know that that the phenotypic ratio is equal to the genotypic ratio = 11 In conclusion, 50% of the couple's children will be born with alleles Ab that is curly, blond hairFavorite Answer In a standard dihybrid cross there are 4 phenotypes which occur with a 9331 ratio, the test cross gives a 1111 ratio A 13 3 = (931)3 so test cross outcome is (111)1 , or 31 C 15 1 = (933) 1 so test cross outcome is (111)1 or 31


Punnett Squares



Solved 7 10 Pts Five Different F1 Dihybrids Were Self Chegg Com
Write the amount of homozygous dominant (AA) and heterozygous () squares as one phenotypic group Count the amount of homozygous recessive (aa) squares as another group 5a Write the result as a ratio of the two groups A count of 3 from one group and 1 from the other would give a ratio of 31 Punnet Square RatioPhenotypes are physical characteristics When ratios are used to describe phenotypes it's called a phenotypic ratio Phenotypic ratio is the number of one phenotype compared to another phenotypeUsing Punnett Squares to Calculate Phenotypic Probabilities IntroductionBackground Punnett Squares are a diagram which biologists use to determine the probability of an offspring having a particular trait Creating a Punnett Square and using it to determine traits of offspring is called performing a cross



Both Phenotypic Ratio And Genotypic Ratio Of F2 Are Same Ina Co Dominanceb Incomplete Dominancec Brainly In
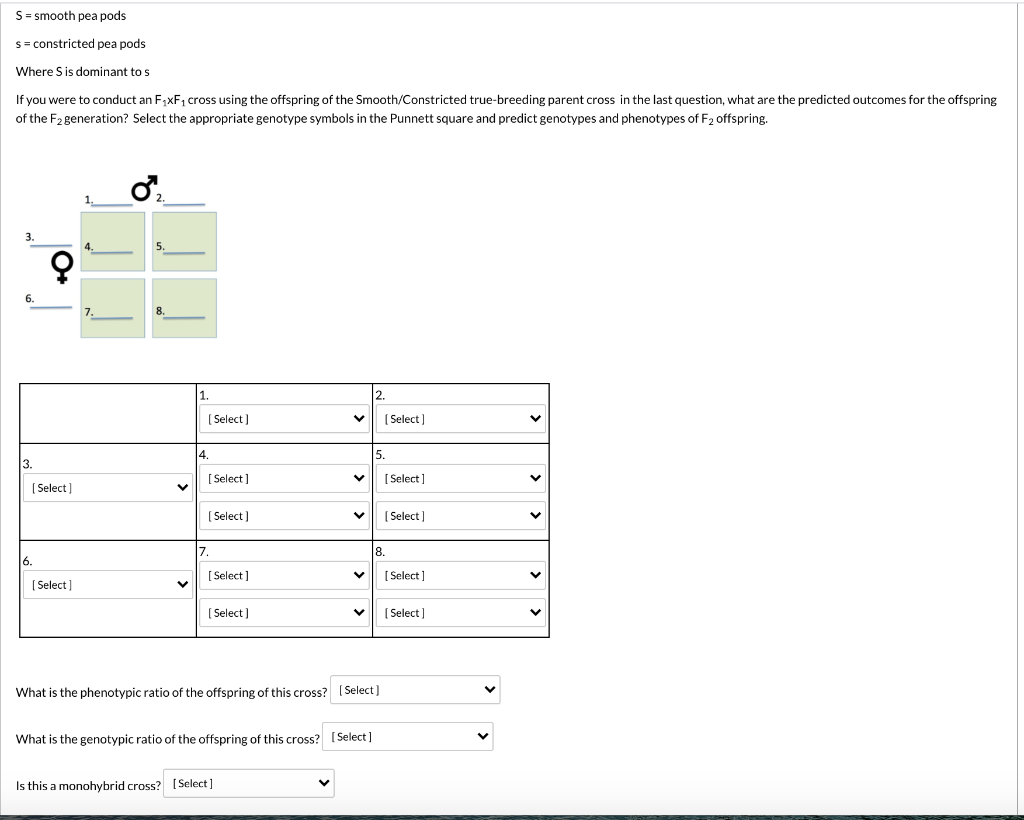


Solved 1 What Is The Phenotypic Ratio Of The Offspring O Chegg Com
The phenotypic ratio is 9331 whereas the genotypic ratio isN The observable physical or biochemical characteristics of an organism, as determined by both genetic makeup and environmental influences The expression of a specific trait, such as stature or blood type, based on genetic and environmental influencesThe genotypic ratios are 1 2 1 2 4 2 1 2 1 for the genotypes AABB AA AAbb BB bb aaBB aa aabb and the phenotypic ratios are 9 " AB" 3 " Ab" 3 " aB" 1 " ab " * Mendel was unaware t hat genes reside on chromosomes Genes that occur on the same chromosome are said to be linked


Q Tbn And9gcrhbjfk65wd V3jjlw37bi3bkqpdzxz21icvc3r23mlc7la3uhx Usqp Cau



Modified Phenotypic Ratio In Lethal Gene Is 1 2 1 2 1 2 1 3
A 9331 phenotypic ratio is characteristic of a Mendelian dihybrid cross That is, a cross between two parents that are heterozygous for two traits See full answer belowIn any case where the parents are heterozygous for both traits ( x ) you will always get a 9331 ratio 9 is the number for the two dominant traits, 3 is the number for a dominant/recessive combination, and only 1 individual will display both recessive traits Another way to determine the ratios is to do it mathematicallyThis means that both parents have recessive alleles, but exhibit the dominant phenotype The phenotype ratio predicted for dihybrid cross is 9331 Of the sixteen possible allele combinations Nine combinations produce offspring with both dominant phenotypes Three combinations each produce offspring with one dominant and one recessive phenotype



Lesson Worksheet Monohybrid Inheritance Nagwa



Which Phenotypic Ratio Would Be Seen In A Cross Where One Gene Is Involved It Has A Completely Dominant Allele One Parent Is Homozygous Recessive And The Other Parent Is Heterozygous Explain
A 9331 phenotypic ratio is characteristic of a Mendelian dihybrid cross That is, a cross between two parents that are heterozygous for two traits See full answer belowHalf of the offspring will be heterozygous (Pp) and half will be homozygous recessive (pp) The phenotypic ratio will also be 11 Half will exhibit the purple flower (Pp) trait and half will have white flowers (pp) When the genotype is unknown, this type of cross is performed as a test crossShading in each Punnett Square represents matching phenotypes, assuming complete dominance and independant assortment of genes, phenotypic ratios are also presented


Http Www Tri Valley K12 Oh Us Userfiles 636 Classes Non Mendelian genetics test review answer key Pdf



Dominance Modification Of Duplicate Genes Leading To A 11 5 Phenotypic Download Scientific Diagram
A phenotypic ratio of 9331 A phenotypic ratio of 9331 is predicted for the offspring of a SsYy x SsYy dihybrid cross 9 spherical, yellow 3 spherical, green 3 dented, yellow 1 dented, green The Biology ProjectThe genotypic ratios are 1 2 1 2 4 2 1 2 1 for the genotypes AABB AA AAbb BB bb aaBB aa aabb and the phenotypic ratios are 9 " AB" 3 " Ab" 3 " aB" 1 " ab " * Mendel was unaware t hat genes reside on chromosomes Genes that occur on the same chromosome are said to be linked


Http Www Gocathedral Com Uploaded Faculty Abrooks Chapter 9 Answers 1 Pdf


Http Web Cortland Edu Biolab 110 Documents Geneticsproblemanswers Pdf



Dihybrid Cross Wikipedia



The Recombinant Phenotypic Ratio In F2 Obtained From Parental Cross Having Genotype Ttrr Ttrr Will Brainly In


Www Graftonps Org Site Handlers Filedownload Ashx Moduleinstanceid 5052 Dataid 8161 Filename 1 trait punnet squares Pdf


What Are The Genotype And Phenotype Ratios Of The F2 Generation Of A Snapdragon Exhibiting Incomplete Dominance For Red And White Flowers Quora


Punnett Squares


Http Bowenstaff Bowen Edu Ng Lectureslides Pdf


Http Endersscience Weebly Com Uploads 2 1 8 4 Punnett Square Practice Answers Pdf


10 2 Dihybrid Crosses And Gene Linkage Bioninja


Www Isd2135 K12 Mn Us Cms Lib Mn Centricity Domain 54 Punnett square key Pdf
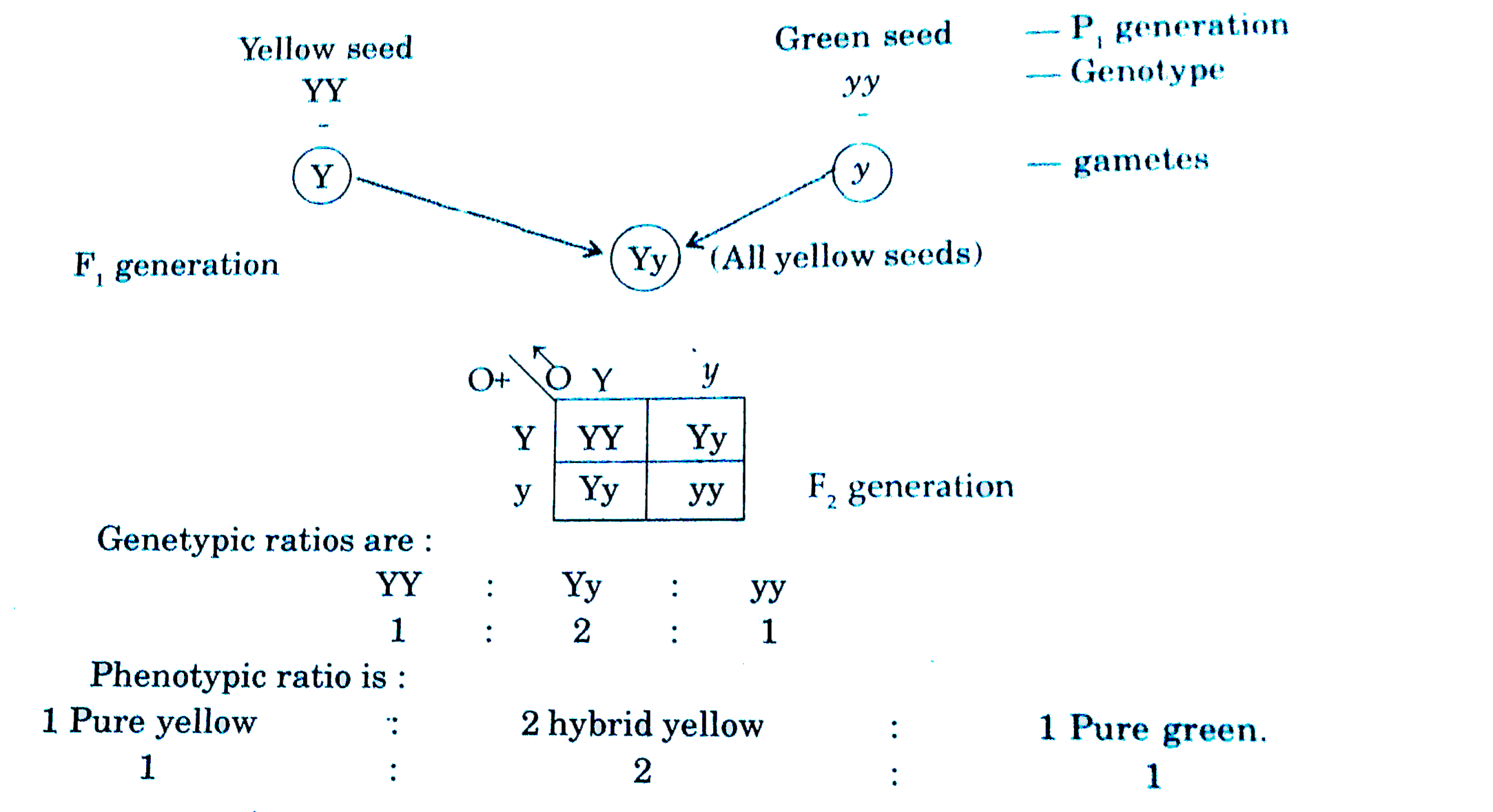


A Explain A Monohybrid Cross Taking Seed Coat Colour As A Trait



Answered Lab Exercises In These Exercises You Bartleby



Solved At Would Be The Genotypic And Phenotypic Ratios Fo Chegg Com



Phenotypic Ratio The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary



Explain The Genotypic Phenotypic Ratio Of Dihybrid Cross With An Example Science Heredity And Evolution Meritnation Com


Http Www Csun Edu Cmalone Pdf360 Ch04 2extensions Pdf


Bil 250 Lecture 3



What Are The Differences Between Phenotypic And Genotypic Ratios For A Dihybrid Cross Quora


How Did You Get A Genotype Ratio In Mendel Dihybrid Cross Quora


Difference Between Phenotype And Genotype Ratio Compare The Difference Between Similar Terms



Monohybrid And Dihybrid Cross



Phenotypic Ratio The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary



7 Find The Genotypic Ratio Genotypic Ratio 8 Find The Phenotypic Ratio Course Hero


Punnett Squares



Part I Monohybrid Cross Question 6 This Questio Chegg Com



Biology 111g Chapter 11 Concept Checks And End Of Chapter Review Flashcards Quizlet


Monohybrid Crosses


If You Were To Perform A Pea Plant Dihybrid Cross Like Gregor Mendel What Would You Expect The Phenotypic Ratio Of Offspring To Be Draw It To Know It


The Phenotypic Ratio Of Red bb And White bb Kernel In F2 Generation Showing Polygenic Inheritance Is Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community



A Classic Mendelian Example Of Independent Assortment The 9 3 3 1 Phenotypic Ratio Associated With A Dihybrid Cross ee ee Learn Science At Scitable



Lmzw 4hohofg0m


Monohybrid Crosses Google Slides


How To Find Phenotypes Ratios As A Result Of Dihybryd Cross Youtube


2



Solved The Phenotypic Ratio Of A Monohybrid Cross Is 31 121 4 Self Study 365


Why Are F2 Phenotypic And Genotypic Ratios Same In A Cross Between Red Flowered Snapdragon And White Flowered Snapdragon Plants Sarthaks Econnect Largest Online Education Community


Q Tbn And9gcrjjful92qnjxyqltzbfoeqrq5cy6czg8eqzm Ndkb0cmgaskwm Usqp Cau



Answers To Genetics Problems


Pinkmonkey Com Biology Study Guide 7 5 Monohybrid Ratio



Phenotypic Ratio The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary
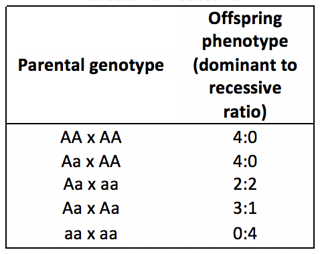


Tips For Interpreting Pedigree Charts And Understanding Inheritance Patterns



Punnett Squares Traits P Parental Generation Genotype Tt Or Tt Gametes T Or T F1 First Filial Generation Genotype Tt Gametes T Or T F2 Second Ppt Download
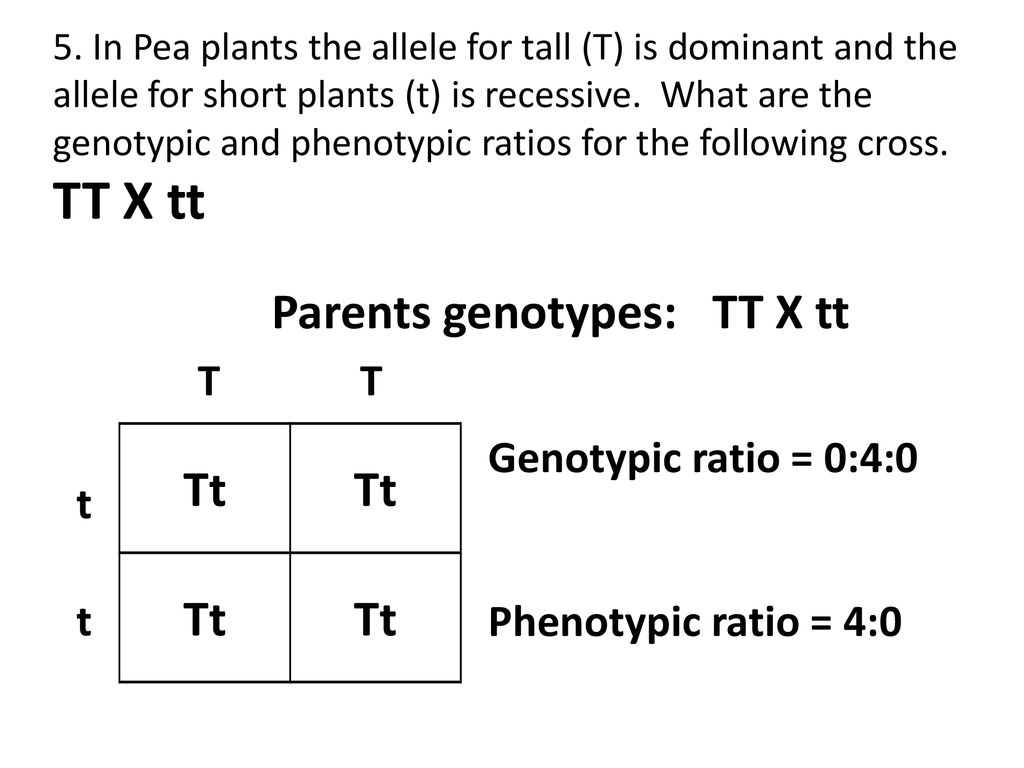


Sample Monohybrid Crosses Ppt Download


3



How To Find Genotype Phenotype Ratio In F1 Youtube



When Predicting The Phenotypic Ratio Of A Crossing Between Two Heterozygous Fruit Flies The Ratio Was Homeworklib



From The Following Table Write The Phenotypic Ratio Brainly In


Www Isd2135 K12 Mn Us Cms Lib Mn Centricity Domain 54 Punnett square key Pdf



Write The Phenotypic And Genotypic Ratios Of Mendel S Cross Pollination Experiments In Pea Plants With Heterozygous Yellow Seeds Yy With That Of The Same Type I E Yy
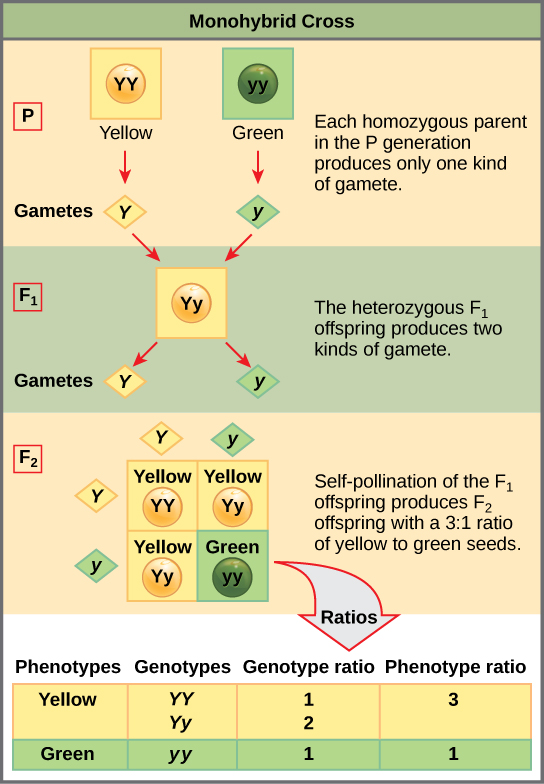


Patterns Of Inheritance Boundless Biology



Dihybrid Crosses Definition Examples Expii


Www Greeleyschools Org Cms Lib2 Co Centricity Domain 5219 Punnett sq cheat sheet Pdf


Dihybrid Cross



Chapter 3 Genetics Page 5 Of 8 Drgp Institute
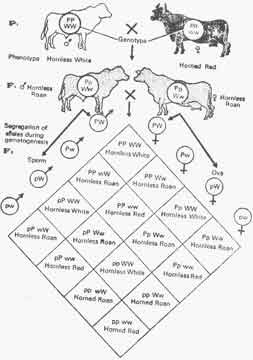


Geneticsstudy Modification Of Dihybrid Phenotypic Ratio



Genotypic Ratios And Phenotypic Ratios For Punnett Squares Youtube



Determining Genotypes And Phenotypes Using Punnett Squares Free Homework Help


Monohybrid Cross Genotypic Versus Phenotypic Ratio Science Biology Genetics Showme



Phenotypic Ratio The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary


Www Greeleyschools Org Cms Lib2 Co Centricity Domain 5219 Punnett sq cheat sheet Pdf


2



Genotype Vs Phenotype Ratio Page 1 Line 17qq Com



Phenotype Ratio Example
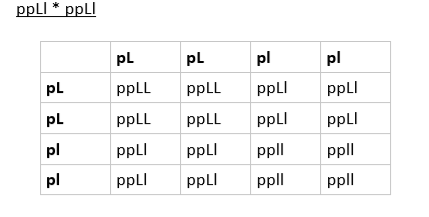


Q What Will Be The Phenotype Gnotype Ratio If We Cross P P L L P P L L Socratic



Genotypic Ratios And Phenotypic Ratios For Punnett Squares Youtube



Phenotype Ratio Examples Page 1 Line 17qq Com
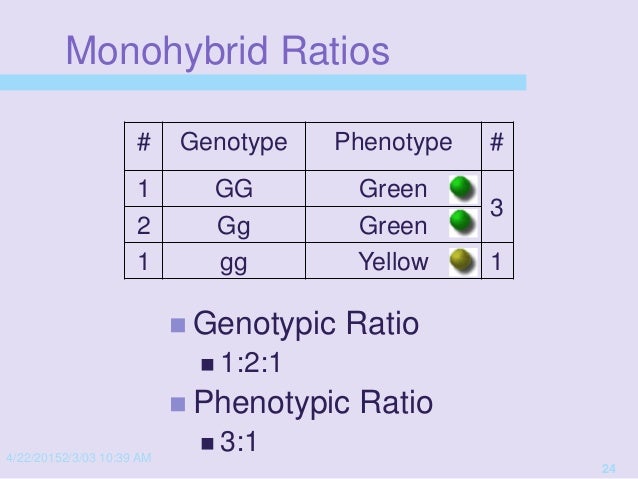


Genetics Presentation 15
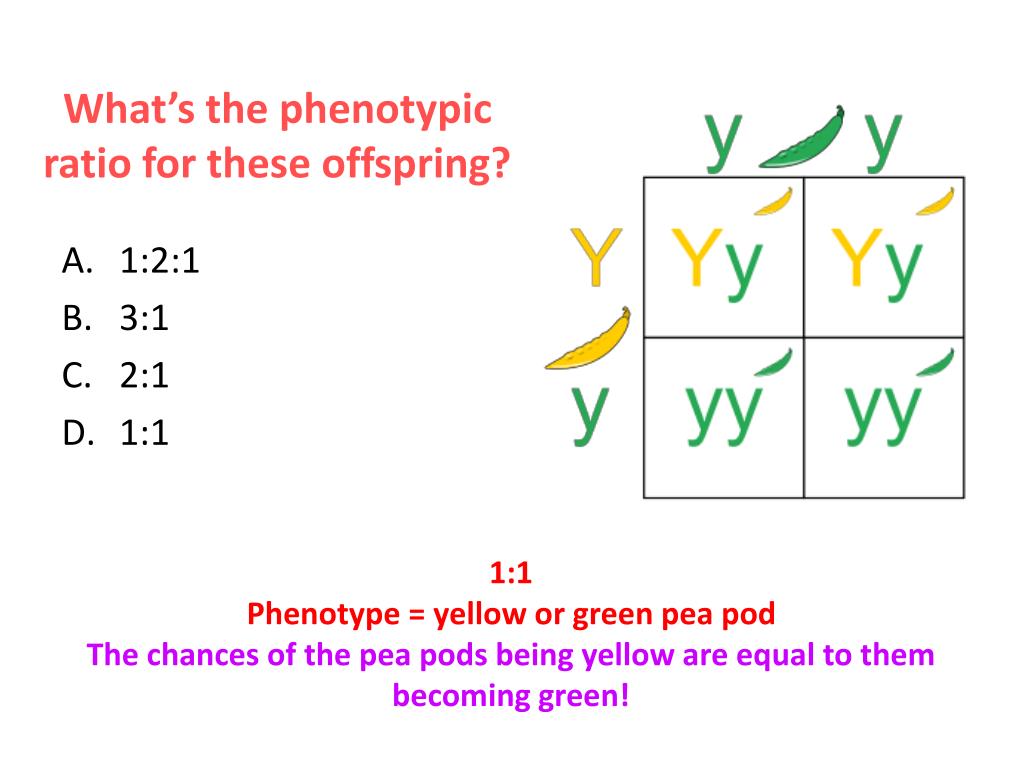


Ppt Mendelian Genetics Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id


Www Gardencity K12 Ny Us Site Handlers Filedownload Ashx Moduleinstanceid 7776 Dataid 8677 Filename Genetics chi Square answer key Pdf



The Ratio Of Phenotype In F 2 Generation Of A Dihybrid Cross Is
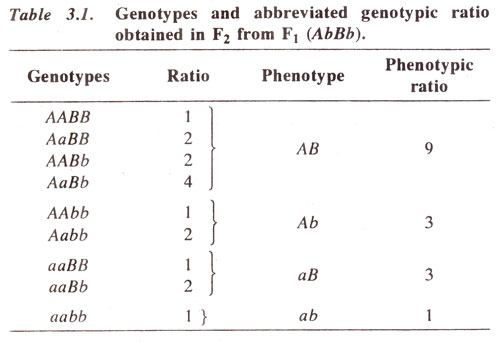


Abbreviated Genotypic Ratio Lethality And Interaction Of Genes


Www Lths Net Site Handlers Filedownload Ashx Moduleinstanceid Dataid Filename Dihybrid cross problems page 2 3 Key Pdf



Dihybrid Cross Phenotypic Ratio White Background Stock Illustration



Practice Dihybrid Crosses
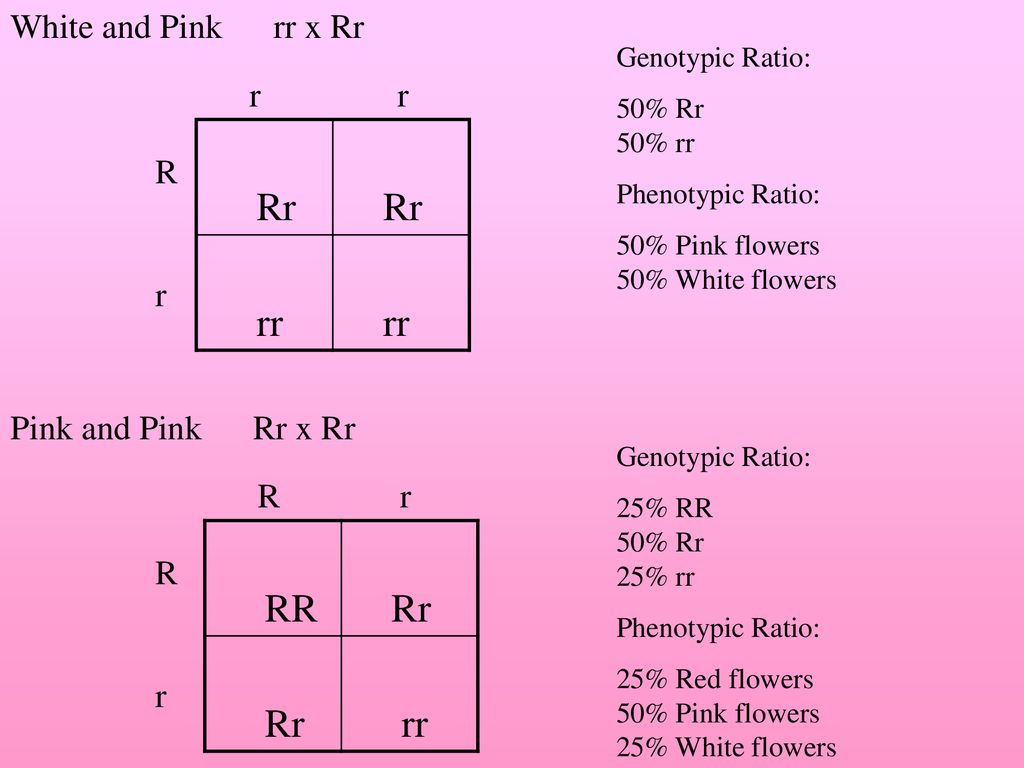


Incomplete Dominance Incomplete Dominance The Heterozygous Genotype Produces A Phenotype That Falls In Between The Dominant Trait And The Recessive Trait Ppt Download



In A Monohybrid Cross Involving Incomplete Dominance The Phenotypi
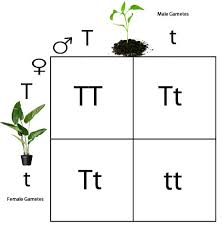


What Is A Genotype And Phenotype Ratio Example


コメント
コメントを投稿